Whereas active process involves expenditure of energy During endocytosis, the cell membrane engulfs materials and a3 How do exocytosis and endocytosis differ from passive and active transport?The difference between active and passive transport is that active transport requires _____, while passive transport does not 2 Define Active Transport Active transport is the process of moving molecules across a cellular membrane through the use of cellular energy How do these meanings relate to the meaning of exocytosis and

Active Transport And Passive Transport Across A Cell Membrane Studypk
Exocytosis active or passive transport
Exocytosis active or passive transport-Biology Movement In and Out of Cells Endocytosis and Exocytosis 1 Answer Rawda Eada yes because in both cases vesicles are formed to the inside of the cell and this vesicle formation is an energy consuming process Explanation To form aThree Types of Endocytosis Active transport moves ions from areas of low concentration to areas of high concentration Endocytosis is a form of active transport that is used to bring large molecules into the cell Phagocytosis is when a cell surrounds




Biology Ch 3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Youtube
Exocytosis is neither passive nor active transport Exocytosis and endocytosis are different ways of moving particles and are nothing like active and passive transport Endocytosis is active engulfing, an example of bulk transport The transport of substances into the cell or from the cell into the external medium may be passive or active process Passive process does not involve any expenditure of energy;The function of phagocytosis is to ingest solid particles into the cell Phagocytosis is a type of endocytosis, which is when cells ingest molecules via active transport as opposed to molecules passively diffusing through a cell membrane
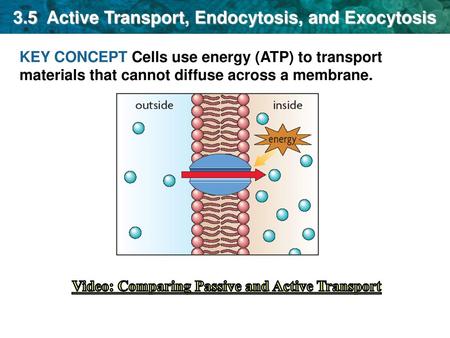
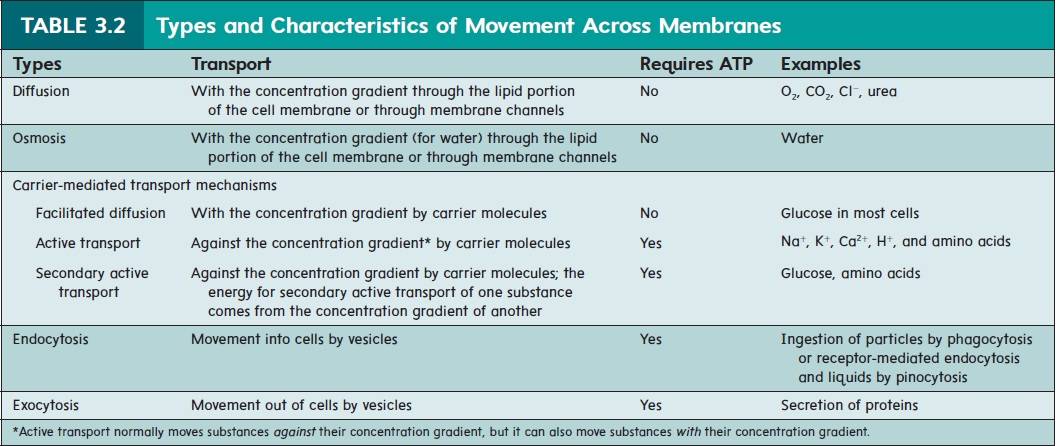
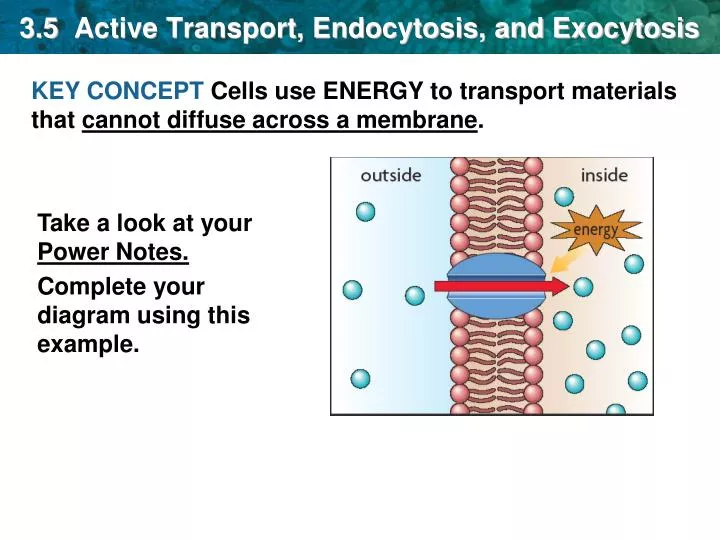
Substances that can not diffuse across the cell membrane must be helped across by passive diffusion processes (facilitated diffusion), active transport (requires energy), or by endocytosis Endocytosis involves the removal of portions of the cell membrane for the formation of vesicles and internalization of substancesWhile exocytosis allows waste material to be packaged and removed from the cell, it also allows various molecules (eg protein) to be transported out of the cell so that they can be used elsewhere These molecules can be used to send signal molecules (eg hormones) to other cells which allows them to respond appropriatelyAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators
In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be teaching you about membrane transport mechanisms These will include the normal physiology of simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport, secondary active transport, pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor mediated endocytosis, and exocytosis!Exocytosis describes the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell Both endocytosis and exocytosis are active transport processesActive Transport Endocytosis Endocytosis is the process of a substance entering a cell without passing through the cell membrane Endocytgosis is seperated into three differnt parts in each transport the formation of a small structure by virtue of the invagination The different catagories differ in the exact mechanisms by which this




Ch5 P94 Types Of Transport Passive Transport Diffusion Osmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Cell Membrane Pumps Endocytosis Exocytosis Movement Ppt Download



1
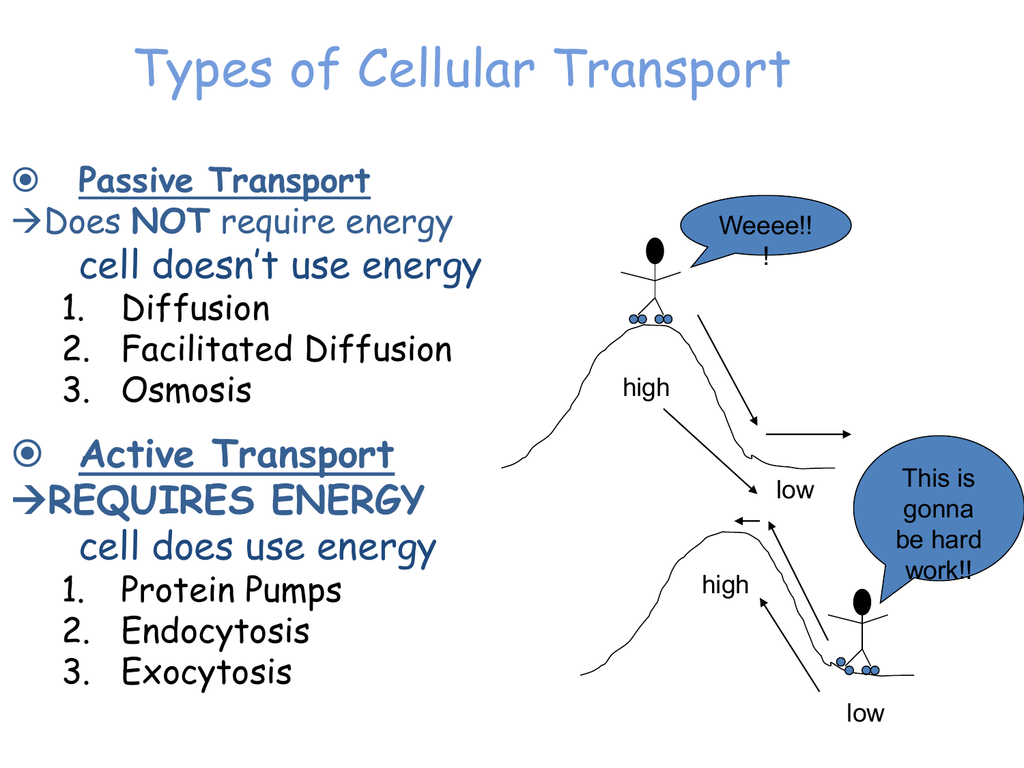
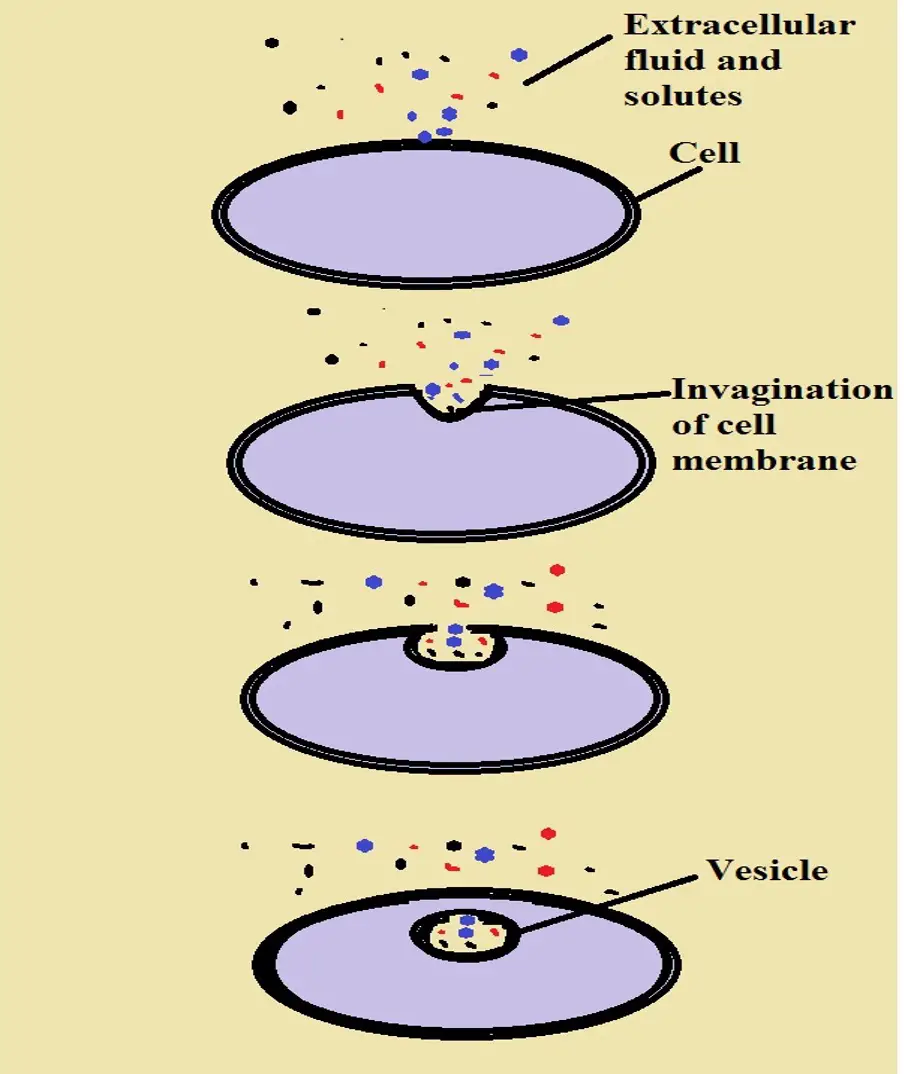
Diffusion is a form of ACTIVE/PASSIVE transport Passive Exocytosis is a process by which materials are exported out of the cell via secretory vesicles In this process, the Golgi complex packages macromolecules into transport vesicles that travel to and fuse with the plasma membrane This fusion causes the vesicle to spill its contents2 Active Transport A)Endocytosis B)Exocytosis 1 Passive Transport = High to low concentration (no energy) Cell Transport Tutorial Cell Transport Review animation and questions Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell This process requires energy and is therefore a type of active transport Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis In endocytosis, substances that are external to a cell are brought into the cell




Solved Fusion Of A Vesicle Containing Secretory Protein With Chegg Com




Exocytosis Wikipedia
Membranes Movement of materials across the plasma membrane occurs by (1) simple diffusion for lipid soluble and small uncharged molecules;Results Pulse experiments with metabolic inhibitors and culturing at 4°C demonstrated the predominantly passive nature of PLGANP uptake Chase experiments with metabolic inhibitors indicated the role of active exocytosis in the extrusion of these NPsExocytosis The reverse process of moving material into a cell is the process of exocytosis Exocytosis is the opposite of the processes discussed in the last section in that its purpose is to expel material from the cell into the extracellular fluid Waste material is enveloped in a membrane and fuses with the interior of the plasma membrane
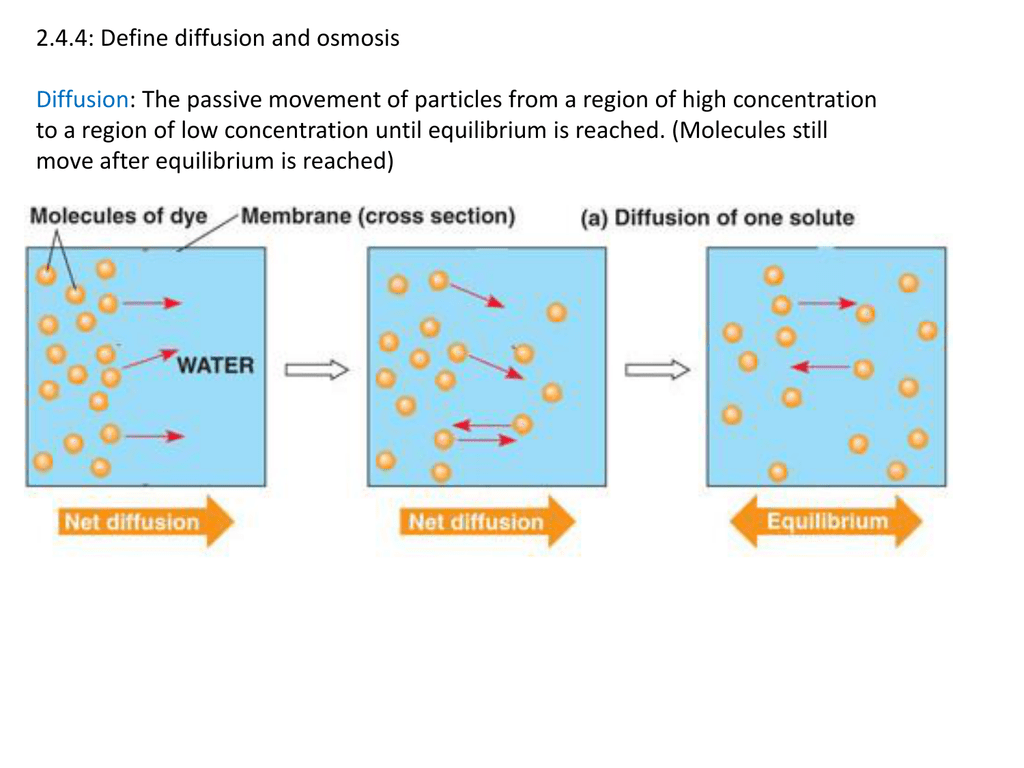



Ib Question Hs Biology Ib
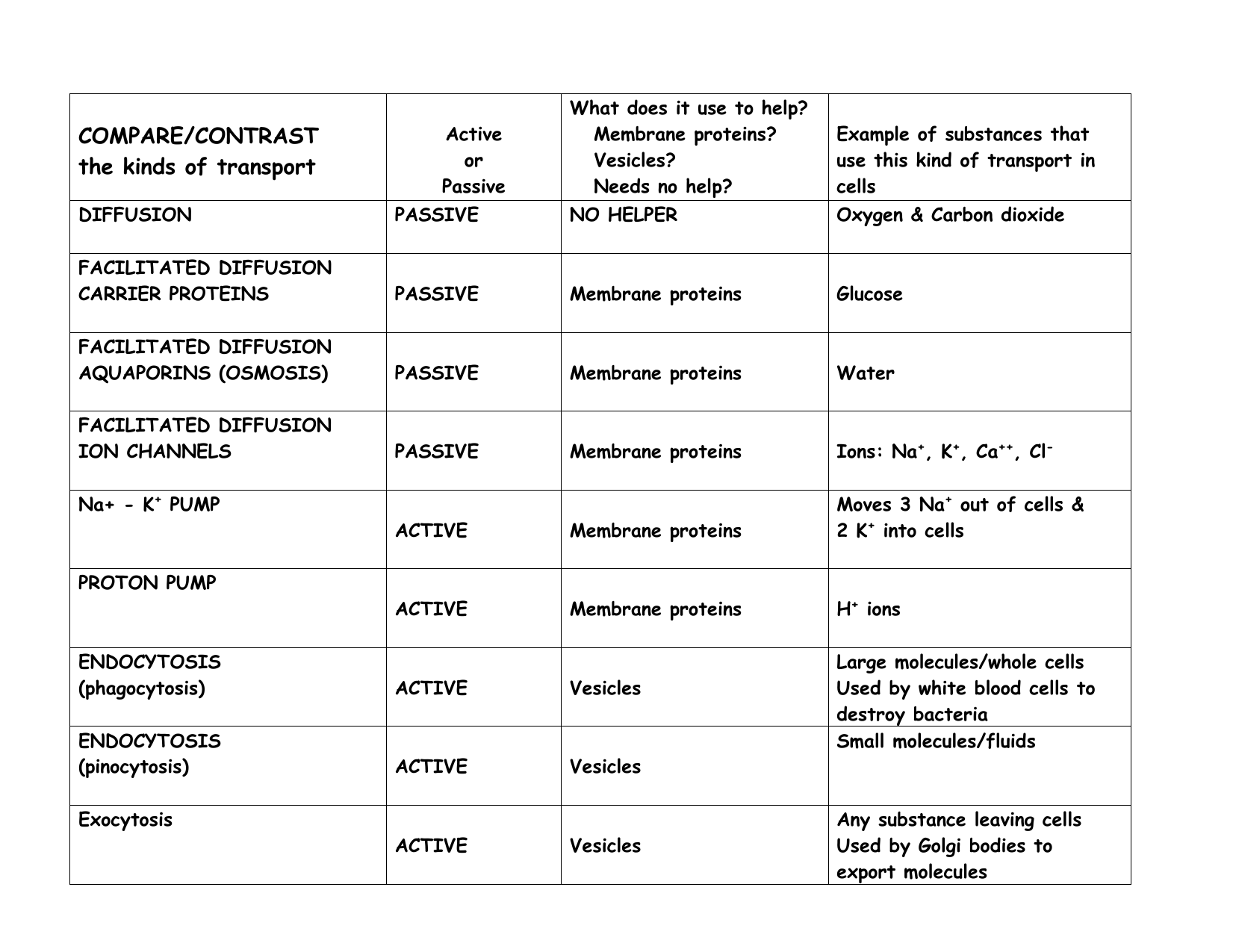



Compare The Kinds Of Transport
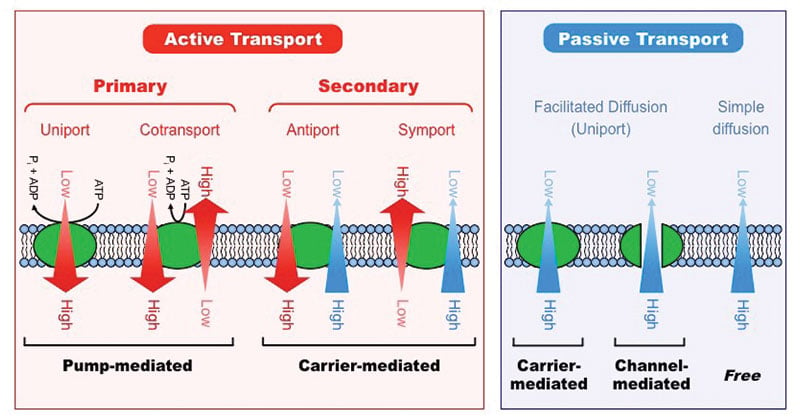
Active Transport Active transport is the movement of molecules across a cell membrane in the direction against their concentration gradient, going from a low concentration to a high concentration Active transport is usually associated with accumulating high concentrations of molecules that the cell needs, such as ions, glucose and amino acids Exocytosis is passive transport or active transport?Active Transport Endocytosis, Phagocytosis, and Exocytosis Watch later Share Copy link Info Shopping Tap to unmute If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device Up next




Different Types Of Exocytosis Endocytosis And Coupling Factors In Download Scientific Diagram




File Exocytosis Types Svg Wikimedia Commons
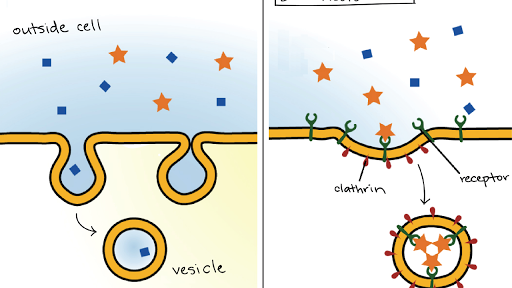
In this lecture Professor Zach Murphy will be teaching you about membrane transport mechanisms These will include the normal physiology of simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion, primary active transport, secondary active transport, pinocytosis, phagocytosis, receptor mediatedEndocytosis Endocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport that move particles into a cell by enclosing them in a vesicle made out of plasma membrane There are variations of endocytosis, but all follow the same basic processWhich is called vesicle transport or bulk transport These processes occur when macromolecules (large molecules) need to be transported




Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary




Biology Notes For A Level 25 Passive And Active Transport Across Cell Membranes
Ungraded Introduction to passive and active transport Endocytosis is the transport of macromolecules, large particles, and polar substances that cannot enter the cell through the nonpolar membrane whereas exocytosis is the transport of molecules or particles outside of the cellIs active transport an example of phagocytosis?Posted on 14 September 21 by gecmisten Exocytosis is passive transport or active transport?




Biology Milestones Active Vs Passive Transport Activity Worksheet




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks
– Let's Answer The World! Active transport passive transport endocytosis exocytosis • transport ions from high concentration to low concentration This is known as simple passive transport because it does not require energy and the water or molecules are moving with the concentration gradient In multicellular organisms there are two types of exocytosis 1) Ca2 triggered nonconstitutive and 2) non Ca2 triggered constitutive Exocytosis in neuronal chemical synapses is Ca2 triggered and serves interneuronal signalling Constitutive exocytosis is performed by all cells and serves the release of components of the extracellular matrix, or just delivery of newly
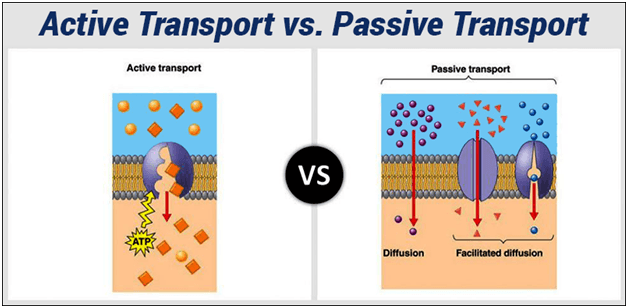



Active And Passive Transport Formative Assessment Quizizz




Active Transport Biology I
Are pinocytosis and phagocytosis examples of active or passive transport?Endocytosis is passive transport or active transport?Explain your answer By signing up, you'll get thousands of




Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Youtube




Exocytosis Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
(2) active or passive transport via membrane transport proteins;Play this game to review Cell Structure The difference in the concentration of solutes between a cell and a solution is Is exocytosis active or passive?




Unit 3 Biology Passive Active Transport Neurons Exocytosis Endocytosis Diagram Quizlet




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
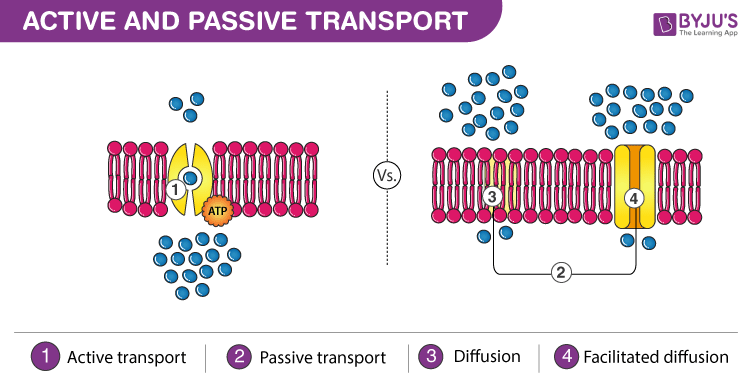
Facilitated diffusion aquaporins (osmosis) Passive Facilitated diffusion ion channels Uses vesicles Helps Endocytosis and Exocytosis Uses membrane proteins Facilitated Diffusion (ion channels, Endocytosis and exocytosis are active transport mechanisms in which large molecules enter and leave the cell inside vesicles In endocytosis, a substance or particle from outside the cell is engulfed by the cell membrane The membrane folds over the substance and it becomes completely enclosed by the membraneMovement Across a Membrane and Energy There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane, and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy, while active transport requires energy to get done Cartoon representing passive transport as rolling a boulder




7 Different Types Of Active Transport Nayturr




1 2 3 Explain What Is Meant By Passive Transport Diffusion Facilitated Diffusion Active Transport Including The Role Of Atp Endocytosis And Exocytosis And The Involvement Of Carrier And Channel Proteins In Membrane Transport
phagocytosis and exocytosis are come from active transport but osmosis and diffusion is from passive transport There is no passive or active transport as such The process involved enveloping Facilitated diffusion and active transport use a carrier or chanel proteien Lyah's Insight I've learned about Passive and Active transport is that passive transport occurs when there is a difference in concentration between substnaces either side of the membranr of cellular tranport wherein substance move against the concentration gradient Endocytosis and exocytosis are the bulk transport mechanisms used in eukaryotes As these transport processes require energy, they are known as active transport processes Vesicle function in endocytosis and exocytosis




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii




Biology Ch 3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Youtube
Passive & Active Transport Endocytosis & Exocytosis Ninja Nerds!Exocytosis and endocytosis differ from passive and transport by using cytoplasmic vesicles to transport through the plasma membrane; Diffusion and osmosis are passive processes whereas active transport and bulk transport are active processes that consume energy Endocytosis and exocytosis are two types of bulk transportation mechanisms, which transport big particles through the plasma membrane, either from cell to the external environment or from the external environment to




Passive Transport Active Transport Exocytosis Endocytosis Membrane Transport Pptx Powerpoint




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
And (3) vesicular transport (endocytosis and exocytosis), which requires readily observable morphological changes in the membraneAnswer to Are exocytosis and endocytosis examples of active or passive transport? Exocytosis Endocytosis Osmosis Diffusion Passive transport Active transport They both are involved in which how the cells membrane reacts to something either ingested or shipped off They both depend on the cell using its energy or not and they both are a form of transport They




Comparison Between Active And Passive Transport Pdf Diffusion Osmosis



1
Exocytosis is the opposite of endocytosis as it involves releasing materials from the cell Exocytosis has five stages, each leading up to the vesicle binding with the cell membrane Many bodily functions include the use of exocytosis, such as the release of neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft and the release of enzymes into the blood The procedure by which cells take up big molecules is called endocytosis and the procedure by which cells release large particles from the cells to the outside is called exocytosis Endocytosis There are two types of endocytosis




Exocytosis And Endocytosis One Student To Another




Ppt 3 5 Passive Transport Vs Active Transport Powerpoint Presentation Id



Emily Compare Active Passive Transport
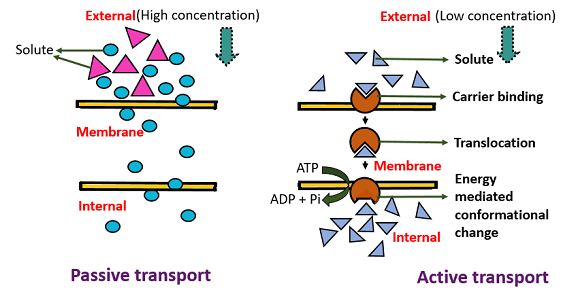



12 Major Difference Between Active Transport And Passive Transport With Examples Viva Differences




Ucx9k4clgftdim




Active Passive Transportation Worksheet
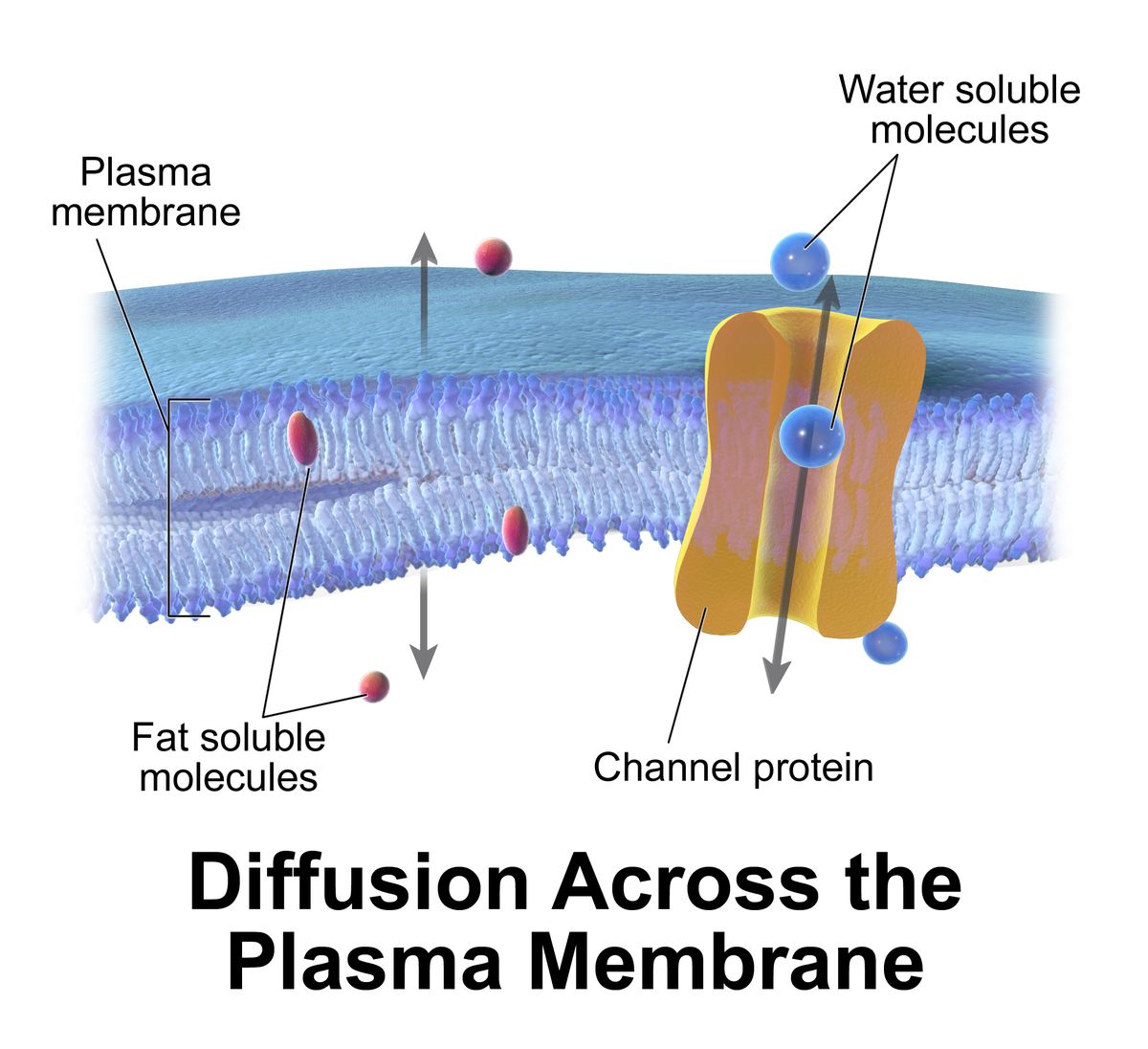



Passive Transport Wikipedia



2 17 Exocytosis And Endocytosis Biology Libretexts




Is Atp Needed For Active Transport Wasfa Blog
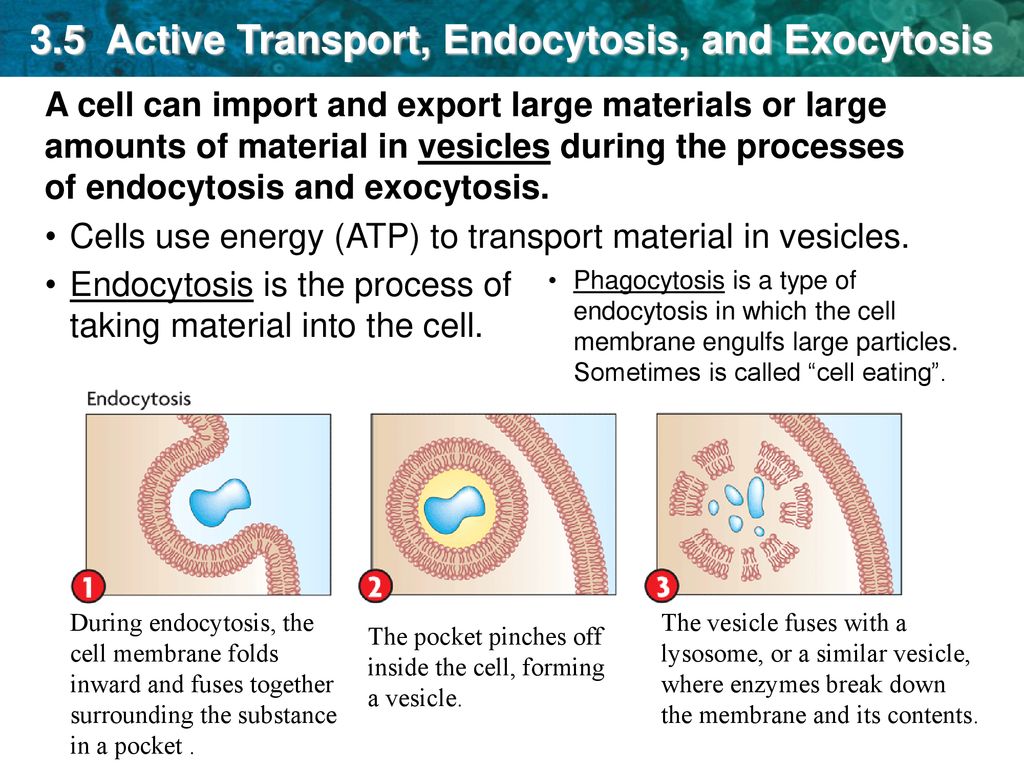



3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download




Cell Transport Active Transport Active Transport Passive Standard




Multiple Choice Questions On Membrane Transport Mcq
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_process-5ae370b4a9d4f900373c9b48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
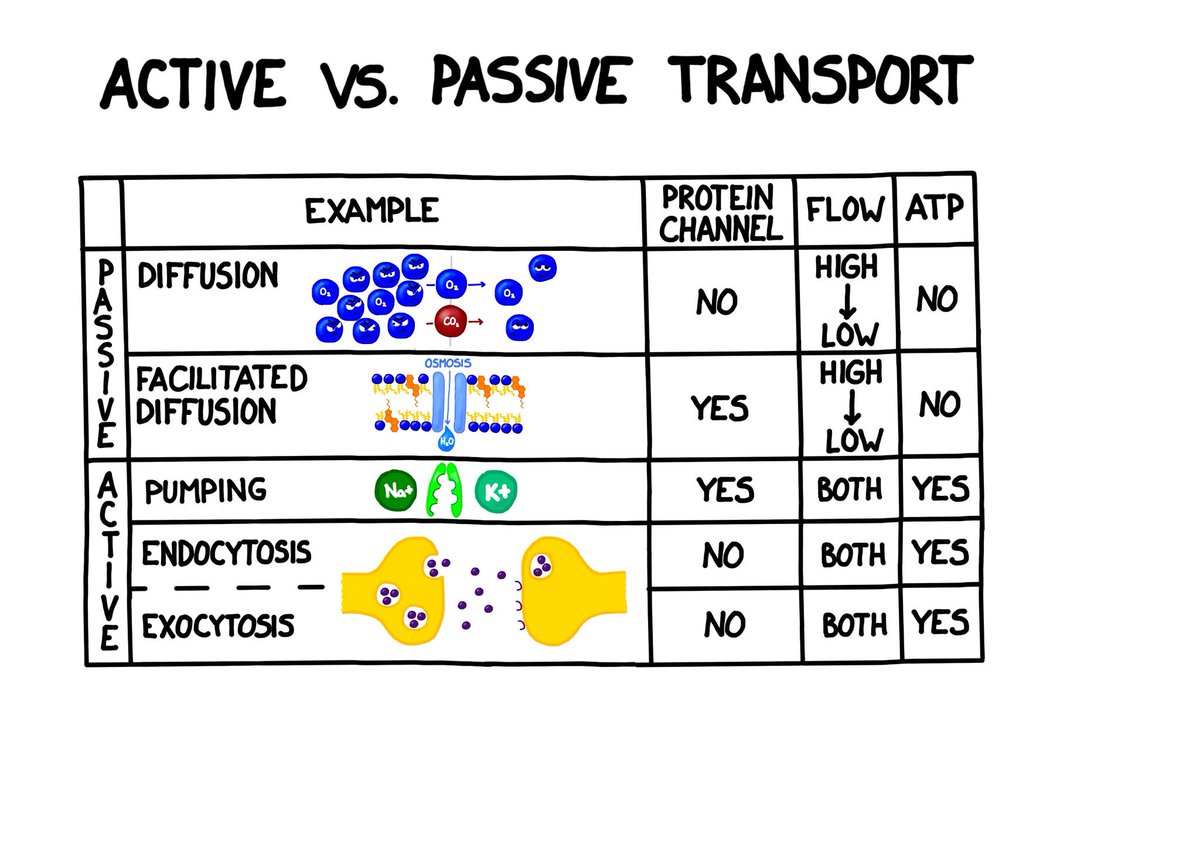



Bogobiology New Video On Active Vs Passive Transport Is Up It Covers Diffusion Osmosis The Na K Pump And Vesicular Transport Active Passive Transport Diffusion Osmosis Sodiumpotassiumpump Endocytosis Exocytosis Apbio



1
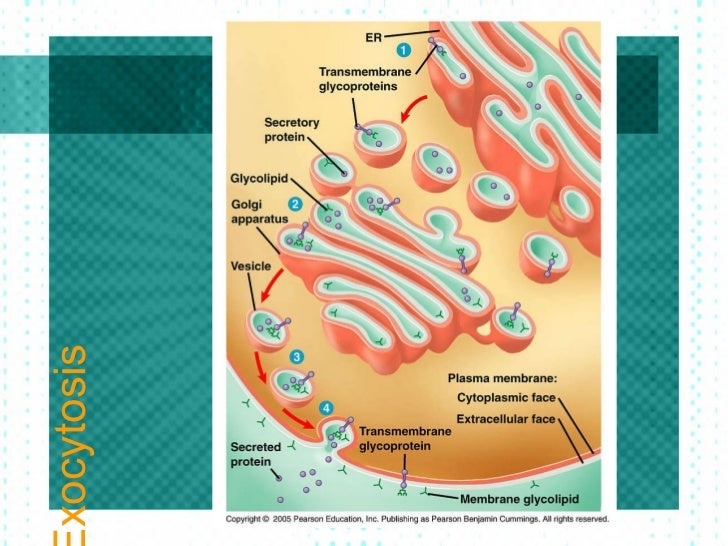



Passive And Active Transport



5 4 Cell Transport



2 4 Membranes Bioninja




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Best One



Transport Of Substances Across Cell Membranes Deranged Physiology




Membrane Transport Passive Transportation Active Transport Phagocytosis Exocytosis
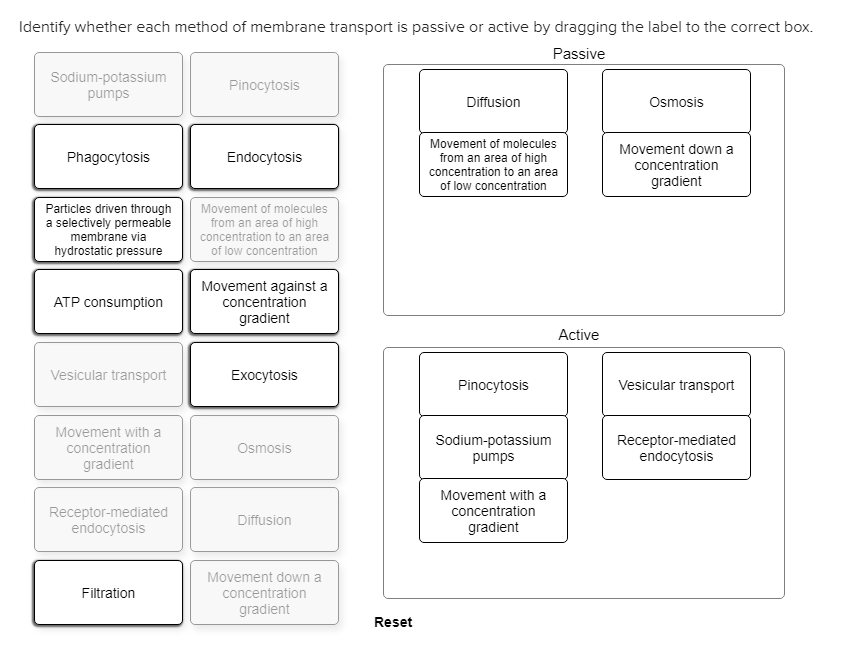



Solved Identify Whether Each Method Of Membrane Transport Is Chegg Com




Passive Transport Across A Membrane Overview Of Passive Active Transport Cell Transport Passive Transport Diffusionosmosis Facilitated Diffusion Active Ppt Download




Active Transport And Passive Transport Across A Cell Membrane Studypk




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




Cell Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis Youtube




7 Cell Organelle Game Ideas Biology Classroom Teaching Biology Science Biology
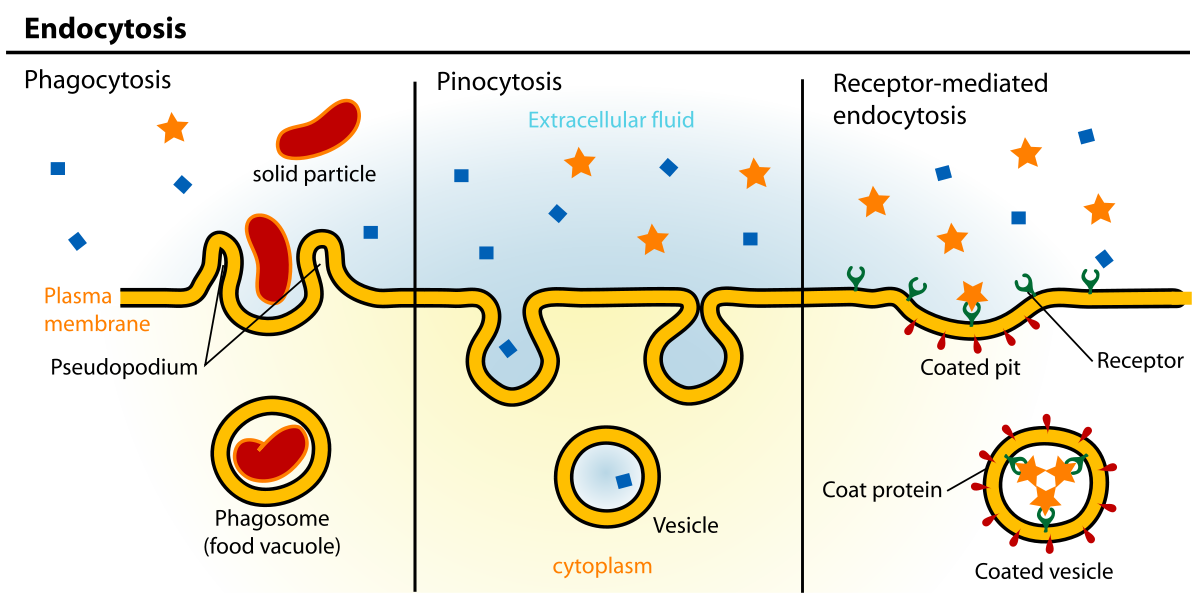



Endocytosis Wikipedia




Transport Across The Cell Membrane Passive Vs Active




Comparison Of Transport Wikilectures




Diffusion Osmosis Exocytosis Endocytosis Active Transport Assive Transport By Kiana Jefferson




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key
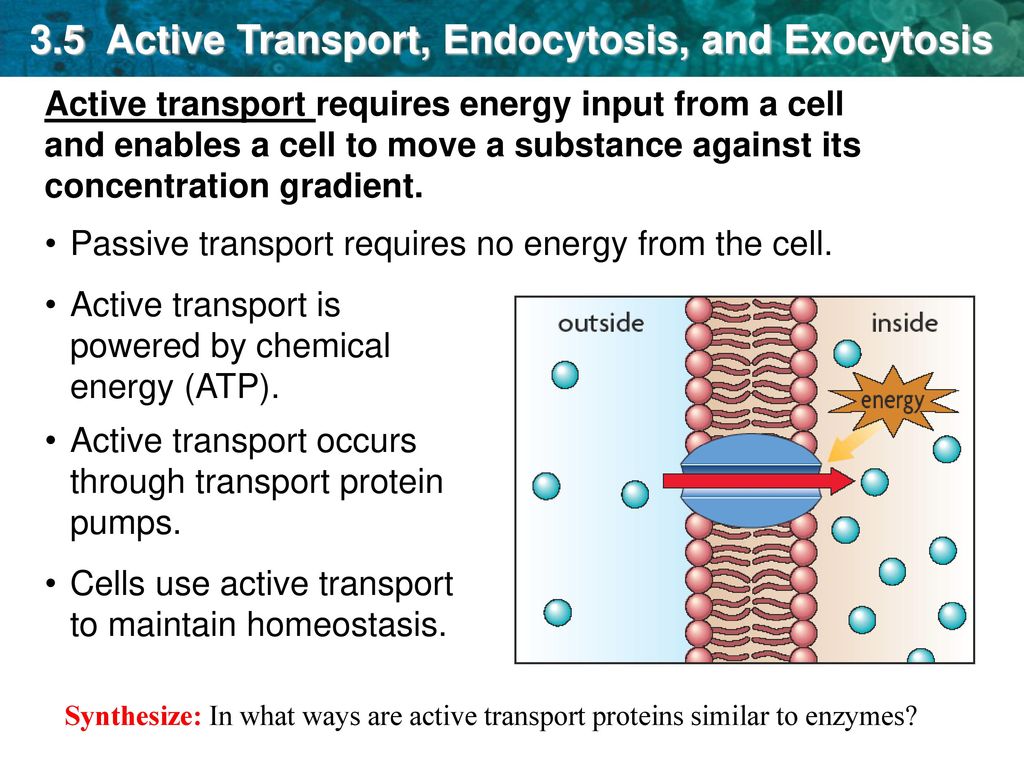



3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download
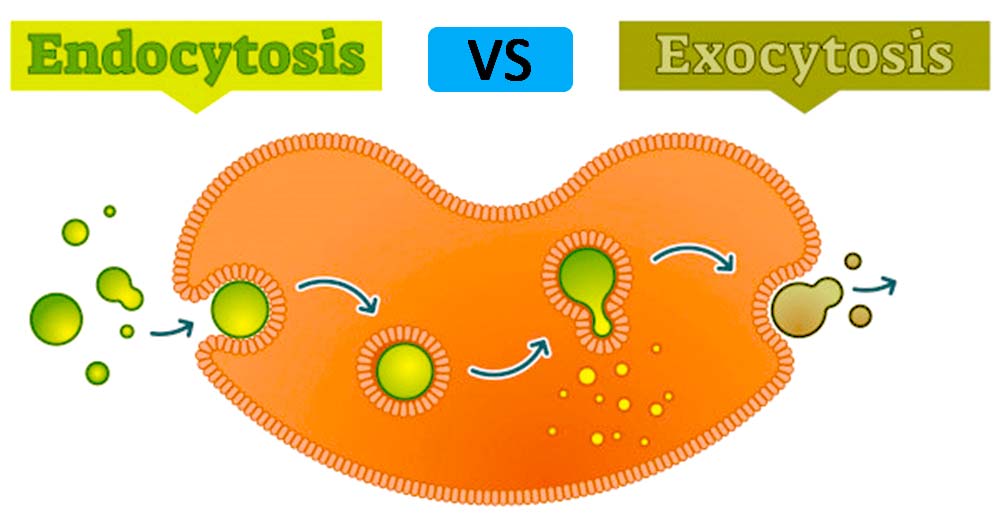



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis




Active And Passive Transport Passive And Active Transport



2



Facilitated Diffusion And Active Transport Ppt




Bogobiology Active Vs Passive Transport Video Tutorial Linked In Bio Osmosis Diffusion Pump Endocytosis Exocytosis Facebook




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Across The Cell Membrane Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download




Filtration Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Passive Transport Transportation Learn Quran



Difference Between Active Transport And Passive Transport




File Transport Across The Plasma Membrane Png Wikimedia Commons



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy
/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples
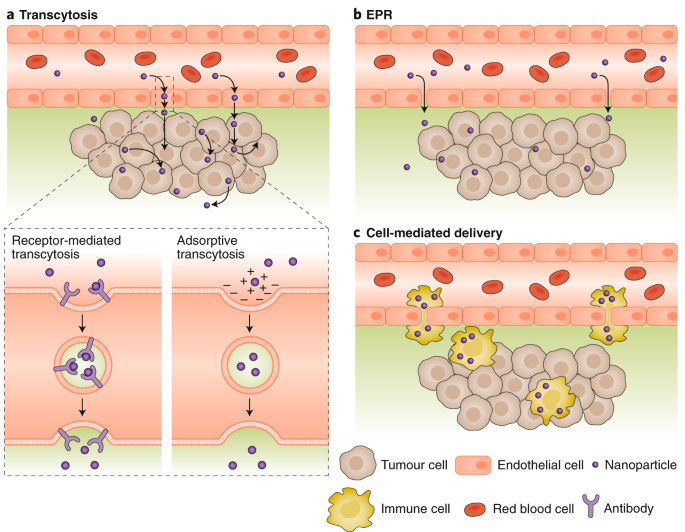



Active Transcytosis And New Opportunities For Cancer Nanomedicine Nature Materials




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key
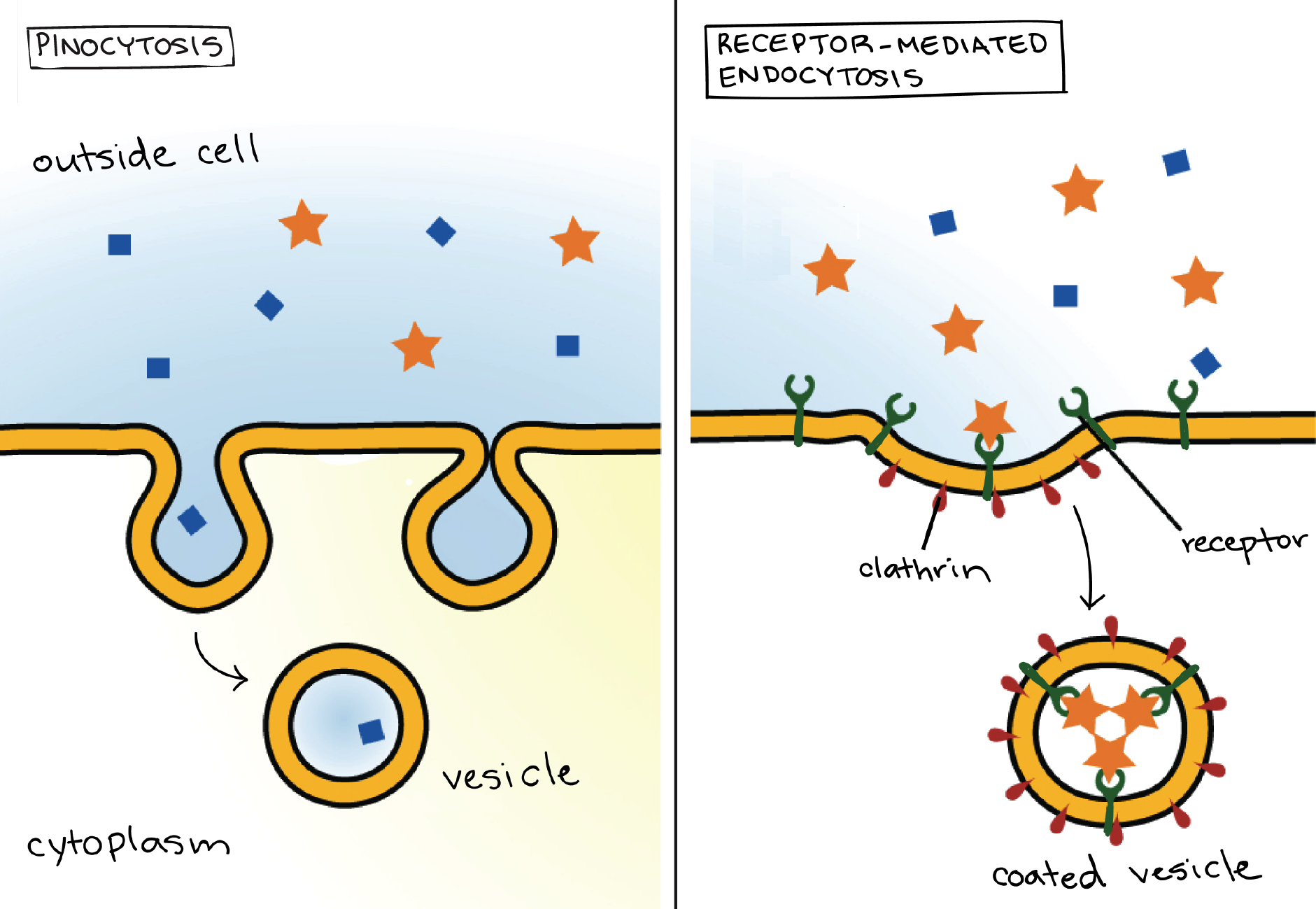



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy




3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Key




Biology Chapter 3 Cell Transport Review Flashcards Quizlet



4 8 Active Transport Human Biology




Ucx9k4clgftdim




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii




Bogobiology Active Vs Passive Transport It S Important That Molecules And Particles Are Able To Easily Move From Place To Place When Transportation Does Not Require Energy Input It S Called Passive Transport




Examples Of Active Transport In Plants And Animals



Ppt 3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Powerpoint Presentation Id
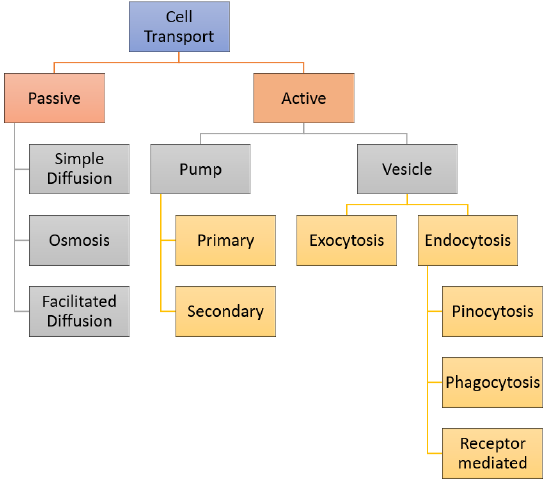



5 7 Cell Transport Biology Libretexts



Movement Through The Cell Membrane



Miguel Compare Active And Passive Transport




Active Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Ocr A Level Biology Teaching Resources




Difference Between Active And Passive Transport In Tabular Form



Endocytosis Diagram



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Types Mechanism Function



Difference Between Active And Passive Transport Definition Types How It Works




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii




Active Passive And Bulk Cell Transport Youtube



Endocytosis Definition 3 Types Active Or Passive Vs Exocytosis



2



Are Exocytosis And Endocytosis Examples Of Active Or Passive Transport Quora




Exocytosis Instagram Posts Photos And Videos Picuki Com



Active Vs Passive Transport Definition 18 Major Differences Examples



Ppt 3 5 Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Powerpoint Presentation Id
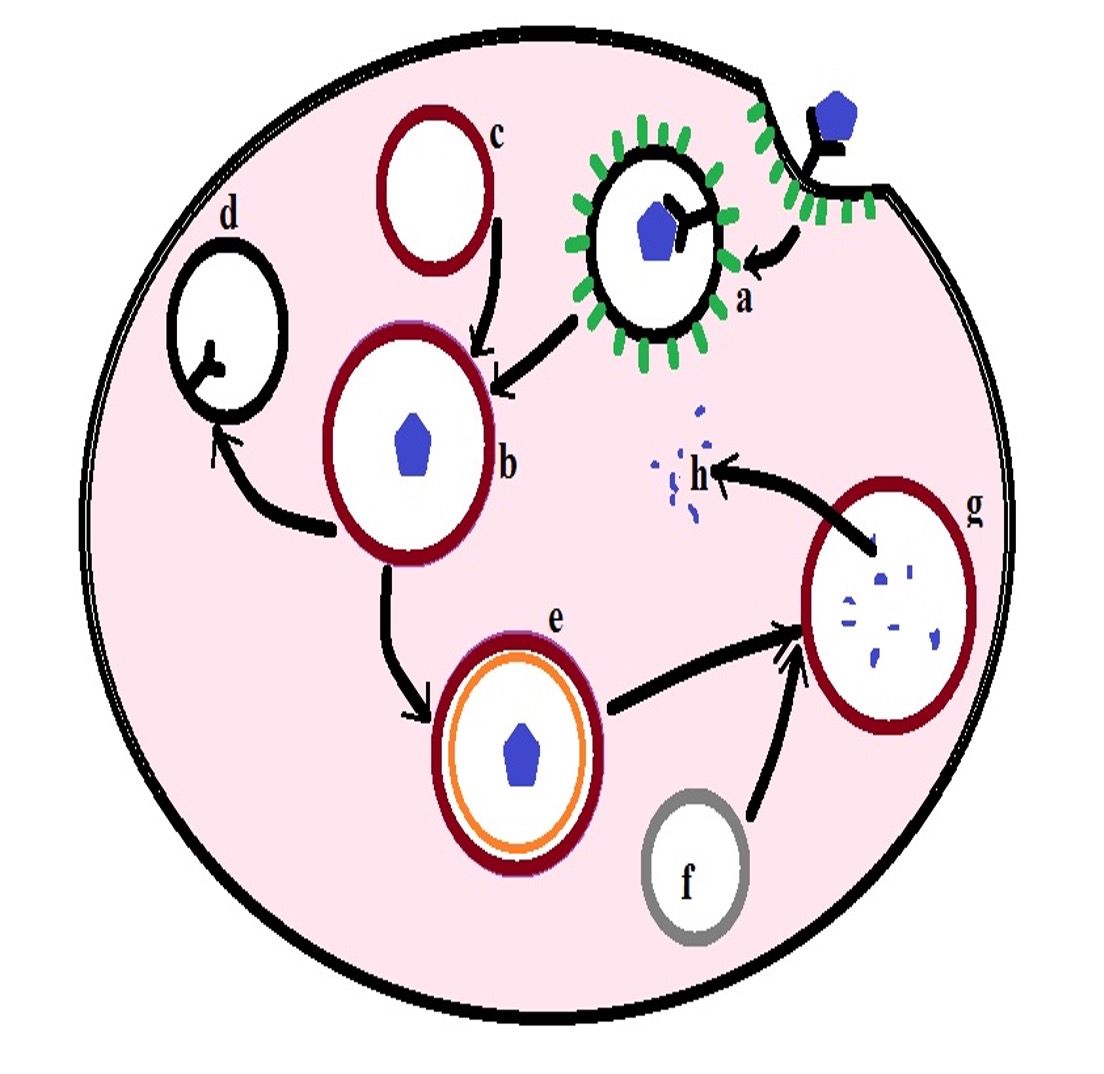



Endocytosis Definition 3 Types Active Or Passive Vs Exocytosis




Active And Passive Transport Difference And Comparison Diffen



2




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks




The Cell Membrane Passive And Active Transport The Biology Primer




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿